Shoulder Osteoarthritis
09/05/2024
最終更新日時 :
03/10/2024
 webmaster
webmaster
椎間板ヘルニアの手術方法、入院日数、保険適用の有無などをご案内いたします。
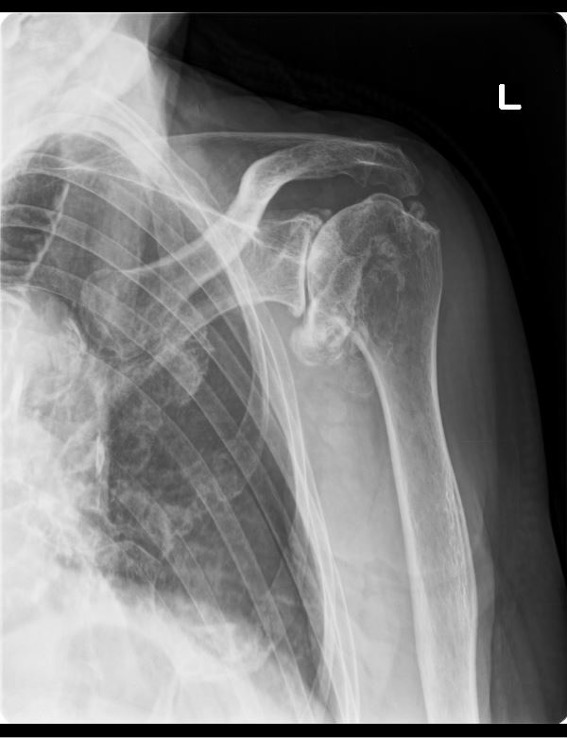
Deformative shoulder osteoarthritis
What is Shoulder Osteoarthritis?
It occurs when the cartilage and bones on the joint surfaces of the scapula and humerus that make up the shoulder joint become painful.
Symptoms
Pain is felt when moving the shoulder, and as the condition progresses, the range of shoulder motion becomes limited. It can also develop after rotator cuff tears, fractures, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment methods
Treatment options include oral medications, shoulder joint injections, and rehabilitation. If surgery is required, an artificial shoulder joint replacement may be performed.
Surgical methods
- Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (TSA)
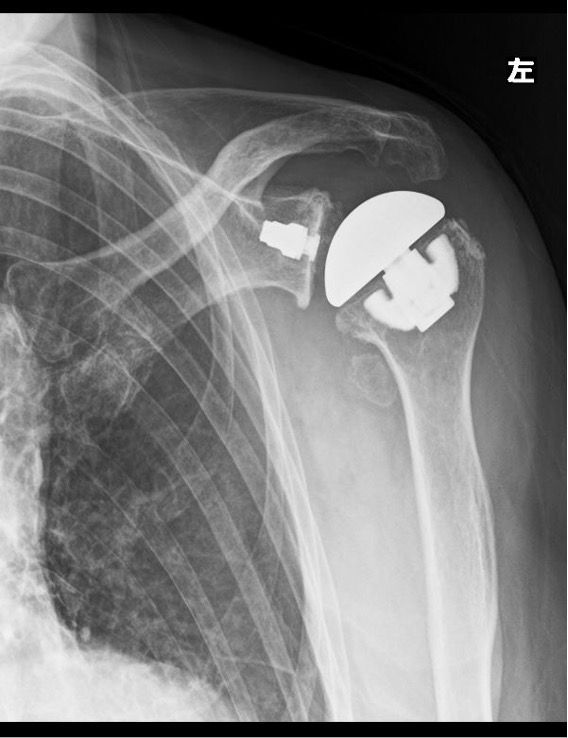
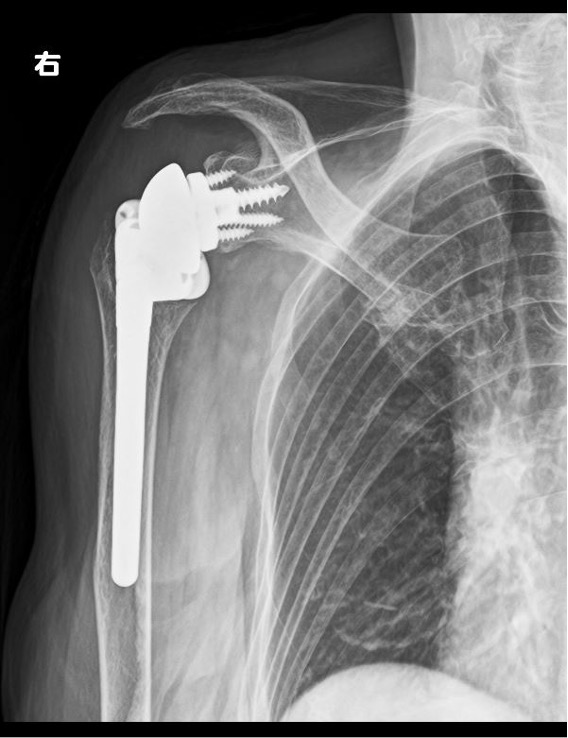
The main difference between the two types of procedures is that anatomical total shoulder arthroplasty requires intact rotator cuff function for effective shoulder elevation. In contrast, reverse total shoulder arthroplasty allows for shoulder elevation through the strength of the deltoid muscle, even if the rotator cuff function is lost. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty can only be performed by surgeons certified by the orthopedic society.
- Disease Name
- Shoulder Osteoarthritis
- Body Part
- Upper Limbs/Scapular Region
- Type of Disease
- Joint Problems